Designing plastic product structures involves considering various factors to ensure functionality, aesthetics, manufacturability, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some key principles to follow when designing plastic product structures:
- Functionality and Purpose:
Clearly define the intended function and purpose of the plastic product. The design should prioritize fulfilling its intended role effectively.
- Material Selection:
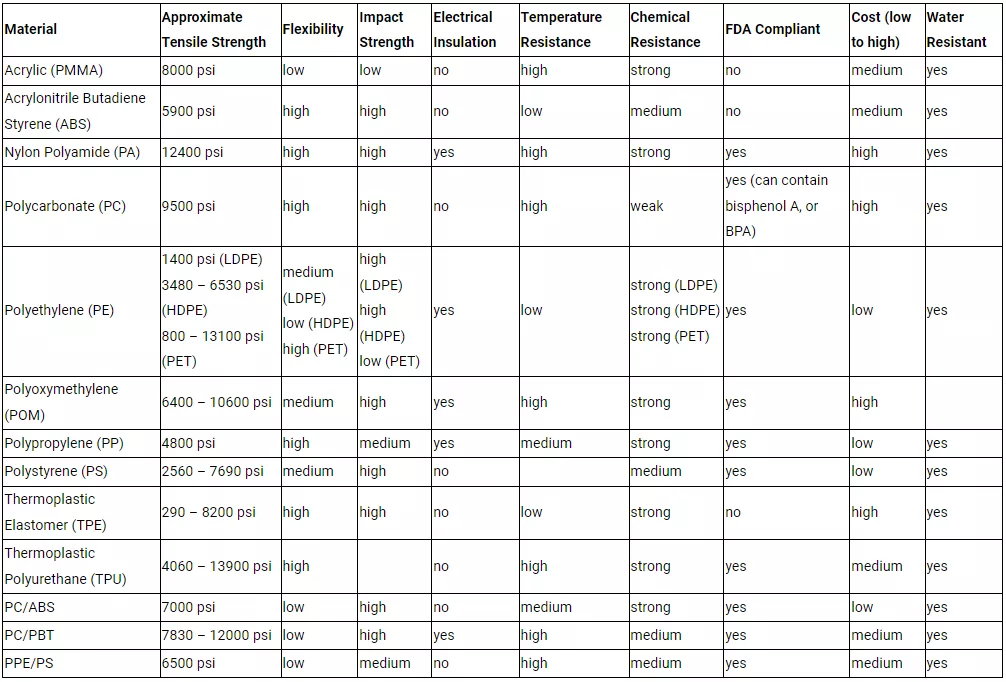
Choose a suitable plastic material based on factors such as mechanical properties, chemical resistance, temperature stability, and appearance.
- Part Geometry:
Design the part with proper dimensions and geometry that ensure functionality while considering factors like strength, rigidity, and assembly requirements
- Wall Thickness:
Maintain consistent and appropriate wall thicknesses to prevent defects like sink marks, warping, and voids during the molding process.
- Ribs and Reinforcements:
Incorporate ribs and reinforcements to enhance structural integrity, minimize flexing or bending, and improve load-bearing capabilities.
- Draft Angles:
Add draft angles to the design to aid in easy ejection from the mold and prevent damage to the part.
- Fillets and Radii:
Introduce fillets and radii at sharp corners and edges to distribute stress, improve aesthetics, and prevent stress concentration points.
- Assembly Considerations:
Design components for ease of assembly, considering features like snap fits, interlocking tabs, and fastening mechanisms.
- Aesthetic Appeal:
Pay attention to the visual aspect of the design. Create a visually pleasing product by considering surface finishes, textures, and any branding elements.
- Tolerances:
Define appropriate tolerances to ensure proper fit and function of assembled parts. Consult with manufacturing experts to determine achievable tolerances.
- Undercuts and Parting Lines:
Avoid complex undercuts that could complicate mold design and increase production costs. Plan parting lines to ensure smooth mold separation.
- Surface Finish:
Specify the desired surface finish to achieve the desired appearance and tactile feel of the product.
- Sustainability:
Consider environmental factors by designing for recyclability, using eco-friendly materials, and minimizing material waste.
- Prototyping and Testing:
Create prototypes to test the design’s functionality, ergonomics, and performance before moving to mass production.
- Manufacturing Process:
Design with the chosen manufacturing process in mind (e.g., injection molding, blow molding). Consult with manufacturing experts to optimize the design for production.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
Strive for a balance between design aesthetics, functionality, and production cost. Minimize complexity and waste to keep costs reasonable.
- User-Centered Design:
Prioritize user experience by considering ergonomics, user interactions, and safety aspects in the design.
By following these principles, you can create plastic product structures that are not only visually appealing but also functional, durable, and suitable for efficient manufacturing processes. Collaborating with experienced designers, engineers, and manufacturers can further enhance the quality of your plastic product design.
