Injection molding is a process of melting plastic pellets. Injection molding manufacturers inject molten plastic into a mold cavity. A pressure is applied to complete the filling following cooling and solidifying the part. In the final step, you open the mold and eject the finished part.
Today, injection molding has become an indispensable. Industries such as automotive, medical, and consumer goods are big consumers. In the following article, you will read the basics of plastic injection molding including process, design, and materials.
The Injection Molding Process Step By Step
Injection molding process is complicated. However, right protocols will result in high-quality plastic parts. Here is a step by step explanation:
Clamping
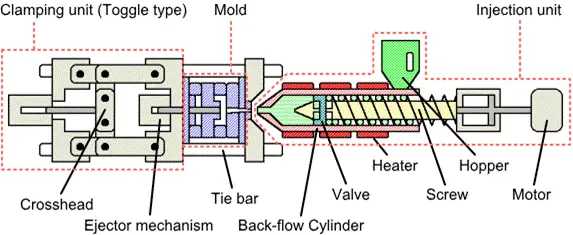
It is cylinder-like mold, which gives the part its shape. Moreover, it has 2 halves,—one stationary and one movable. The mold is then fully clamped shut by a unit that applies a great deal of force before the molten plastic is injected.
This method keeps material from oozing out of the design during this process. The clamping force, measured in tons, ensures the mold is sealed tightly. This is an extremely important step as even the smallest misalignment can cause imperfections in the end product.
Injection
Thermosetting polymers comes in plastic pellets is fed into the barrel of the machine. Inside the barrel, the system of screws or plungers applies heat. It causes the element to melt to plastic. The molten plastic is injected into the cavity of the mold under high pressure. Improper air control can result in defects such as voids and incomplete parts.
Cooling system in injection molding
Going through the process injection, the plastic starts to cool and harden in the cavity inside of the mold. Uniform solidification is ensured by proper cooling. It preserves the geometry and the form of the part.
However, uneven cooling can lead to defects such as warping and shrinkage. This step takes place at different time frames due to the material type and the thickness of molded part.
Ejection
After the part has fully cured, the mould opens, and ejector pins or plates push the part off. The part is carefully ejected to prevent damage. The mold resets and the cycle repeats itself.
Injection Molding Machine Classifications
Hydraulic Machines
Therefore, the hydraulic injection molding machines are the machines using hydraulic operations for various processes. These machines are commonly used for manufacturing large plastic parts.
They are generally used in applications dealing with high-pressure applications such as the automobile and heavy equipment manufacturing industries.
Electric Machines
Electric machines provide a high level of precision and energy efficiency. They work faster than hydraulic machines. You can easily produce small, and complex parts. They are often favoured for more complex designs as they run quieter and do not need a lot of maintenance.
How CAD Influences Mold Design?
Molds are usually designed using CAD software, which engineers use extensively. Before a single door is built, CAD tools offer accurate modeling of the molds simulation. Using these simulations is a way to rectify issues early on such as short flow or cooling.
CAD makes it possible to test molds on computers. It reduces mistakes and saves time.
The Importance of Mold Design
A good-quality mold will ensure the procedure goes smoothly and the components are top-quality. Substandard mold design can result in defects, waste, and increased production costs. Every mold needs to be designed, tested, and constructed to spec for consistent and reliable manufacturing.
Define Part Specification
It all begins with pinpointing the needs of the product. Verifying part dimensions, surface finish, and functional tolerances is the job of the engineers. As an example, a component such as a spur gear typically needs to be toleranced within tight limits to function properly.
But, the design is also in part governed by the environment the part is going into. For instance, you might need to use only certain material or particular wall thickness for components exposed to chemicals or high temperature.
Design 3D Model of the Part
Engineers create a 3D model with CAD software (e.g. SolidWorks or Fusion 360). CAD model is the one with all the necessary parameters like draft angles and uniform wall thickness.
Ejection without damage requires 1°–2° draft angles. Internal stresses and defects are avoided with uniform wall thickness. Thin, uniform walls and intricate contours are essential, for example, in medical device cases.
Design of Mold Cavity and Core
The hollow part and the core are the center of a mold. They represent the outer and inner surfaces of the product. These are developed by engineers on the 3D model. Durable materials such as steel are designed for high-volume production.
But, if you want to do a prototype, or something that maybe you are going to make a very low volume of, aluminum molds work quite well. Shrinkage rates are also factored in, since plastics like polypropylene and nylon shrink differently. This variation is accounted for in the design.
Create Runners, Gates, and Vents
Runners and gates direct liquid plastic into the cavity. Their design affects how uniform the mold fills and how smoothly the plastic flows. They differ in terms of whether you have to keep the plastic molten (hot runner systems) or if they make it more affordable (cold runners).
Typical Temperatures
- Manifold 180-240°C
- Nozzle 200-260°C
- Melt: 220-300°C.
Depending on the shape and size of the product, engineers select the types of gates (pin or edge gates) to use. Air can be vented from the mold during injection.
Design of the Driving Channels
Key Points Cooling channels play an important role in heat control of the mold. These channels circulate either water or oil to absorb the heat from the molten plastic. As regards to complicated molds, conformal cooling channels are frequently 3D printed.
Ejection System Implementation
After the part cools, ejector pins/plates take the part out of the mold. They need to be placed such that they do not leave marks at any functional area in the part. Air ejection systems or coatings to produce a specific surface finish are used for products that have complex details.
This is vital because unfit ejection can spoil the component which will lead to more waste during production.
Simulating and Testing Out the Mold
Engineers simulate the components used in the assembly to design a mold for manufacturing using software such as Autodesk Moldflow before manufacturing. Simulations examine how molten plastic flows through the mold and identifies defects.
For example, the point where two plastic flows meet can create a weak spot. You need to address it during design adjustments. It reduces errors and costs incurred when producing a mold design using virtual testing.
Manufacture the Mold
The final design is translated into engineering drawings suitable for machining. The mold is cut and shaped using CNC machines and Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM). These processes require a lot of precision as any slight imperfection in the mold can lead to incorrect parts. The mould is then either polished or textured to achieve the desired surface finish.
Software for Mold Design
Modern mold design relies heavily on CAD and simulation tools. Using programs like Siemens NX and SolidWorks, engineers are able to develop an extremely accurate design and model flow patterns. SolidWorks Plastics, for example, forecasts plastic flow in the cavity and spot potential issues such as short shots.
Materials Used with Injection Moulding
Injection Molding: The type of plastic in use depends on the application. The first is the main types they are classified into are thermoplastics and thermosets:
Thermoplastics
Examples of thermoplastics are PP, ABS, PE etc. These plastics which is recyclable, durable and pliable. They melt when heated and turn become solid when cooled. Other plastics that include even 100% virgin material include thermoplastics. Thermoplastics are widely used in consumer goods and ev parts.
Thermosetting Plastics
Heat resistance is important to make custom injection mold parts. Epoxy and phenolic resins are heat-resistant thermosetting plastics. Once set they can neither be remolded nor reshaped.These materials are best for electronic components.
Applications of Injection Molding
Injection molding parts used in different fields. These industries range from electric vehicles to medical field. :
Automotive Industry
Dashboard panels, bumpers, engine covers, and other car parts are made using plastic injection molding. Their components weigh less than metal, driving down gas consumption in cars. The process is able to manufacture complex shapes. It minimizes the amount of components that go into a car. ABS and polypropylene are thermally stable and very durable plastics.
Medical Sector
In the medical line, plastic injection molding is used to make syringes, surgical instruments, and packaging of medical devices. Polycarbonate is the common material to make such products.
It is safe for usage in the body and can be sterilized. In fact, injection molding also allows for greater mass-production of disposables.
Consumer Products
Plastic injection molding is also often used to make household products. The common examples are toys, kitchen utensils, and electronic enclosures. It provides a way for manufacturers to produce these high-quality items at cheaper price.
Conclusion
Custom injection molding gives you a lot of benefits but you must contact with a reputable company. Why? This is important to counter issues like high costs and design malfunction.
rjcmold is a leading china-based injection moldig company. It provides fully integrated and end-to-end Injection molding. We do design, tooling and production. Our company specializes in insert and overmolding. It is expert in medical and LSR molding.
FAQs
What is plastic injection molding?
Plastic injection molding machine operator inject melting plastic into a mold to create parts. This is a high-volume manufacturing process.
What is the cost of custom injection mold?
Lowest End (Around $1,000 – $5,000 for tooling). Highest End ($80,000 or more for tooling). Mold complexity, mold material, mold design, and surface finishing are top 3 factors to determine the final cost of any plastic mold.
Is plastic injection molding difficult?
For professional companies, it is not difficult. However, you must require expertise in design, tooling, and processing.
What plastic is used in injection molding?
Many types, including ABS, polycarbonate, polypropylene, and polyethylene.
What is the difference between plastic extrusion and injection molding?
With plastic extrusion, you can make continuous shapes. However, injection molding makes discrete parts.

