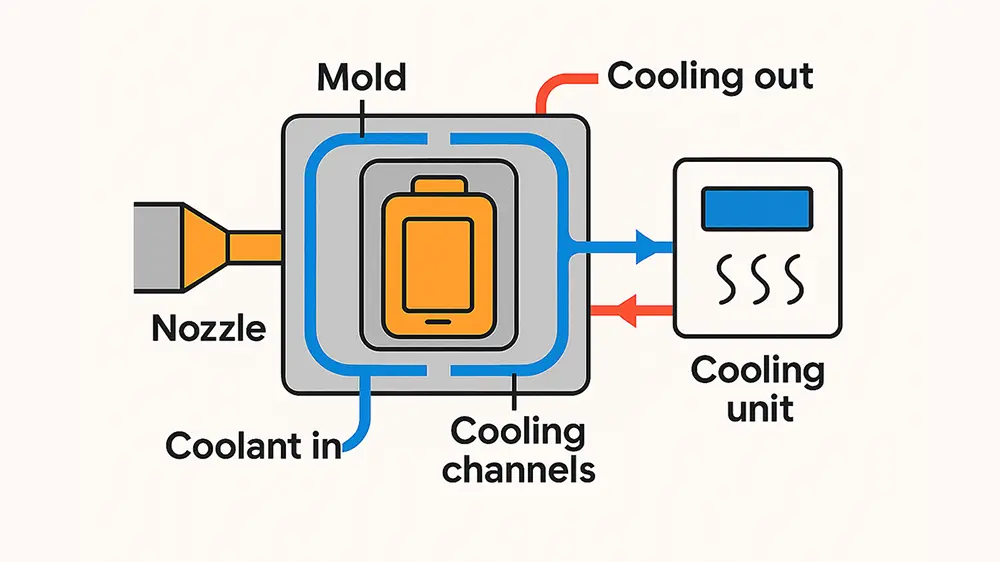
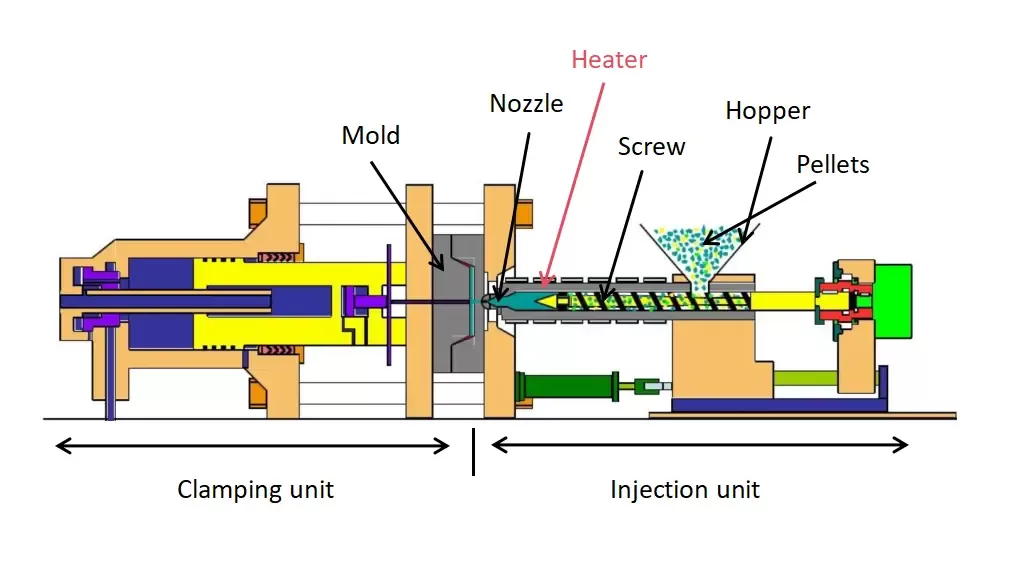
There are many factors influencing injection mold cooling, such as the shape of plastic parts, design of parting surface, type of cooling medium, temperature, flow rate, geometric parameters and space layout of cooling pipes, mold materials, melt temperature, ejection temperature required by plastic parts and mold temperature, thermal cycle interaction between plastic parts and mold, etc. Here we will introduce the effect of mold temperature on injection molded products.
Low mold temperature can reduce the molding shrinkage of plastic parts. In the process of mold opening, it is necessary to overcome the direct mold opening force. During mold opening, there will be a certain adhesive force generated in the direction parallel to the mold opening. The adhesion force is related to the properties of the plastic, the surface quality of the mold, and the draft Angle. In addition, it is necessary to overcome the indirect mold opening resistance, that is, to overcome the pulling resistance in the process of moving side core pulling during mold opening. The friction resistance generated by the movement of the moving template and the moving template is also overcome. Finally, it is necessary to overcome the pressure of the cavity, the cavity pressure may not be equal to the atmospheric pressure, cavity pressure and external pressure is not equal.
The surface quality of plastic parts can be improved by increasing the mold temperature. The determination of mold temperature in the process of injection molding, mold temperature directly affects the plastic mold filling, molding, molding cycle, and plastic parts quality. The mold temperature depends on the crystallization of the plastic, plastic parts size and structure, performance requirements, and other process conditions such as melting temperature, injection speed, injection pressure, and molding cycle.
Uniform mold temperature, short cooling time, and fast injection speed can reduce the warping deformation of plastic parts. For the crystalline polymer, increasing the mold temperature can make the size of the plastic parts stable and avoid the phenomenon of post-crystallization, but it may lead to a prolonged molding cycle and brittle defects of the plastic parts. With the increase of crystallinity of crystalline polymer, the resistance of plastics to stress cracking decreases, so it is beneficial to reduce the temperature of the mold. However, for the amorphous polymer with high viscosity, its endurance cracking is directly related to the internal stress of the plastic parts, so it is beneficial to improve the mold temperature and filling speed and reduce the feeding time.
For amorphous polymers, the melt solidifies with the decrease of temperature after injection into the mold cavity, but no phase transition occurs. The mold temperature mainly affects the melt viscosity, that is, the mold filling rate. Therefore, the melt viscosity is low, and medium amorphous plastics such as polystyrene, cellulose acetate, etc., can use lower mold temperature to shorten the cooling time.