An injection mold tooling cost calculator estimates your price of the mold and scores the largest cost factors, including the tool material, the number of cavities, the complexity of the part, and the required life span of the tool. This gives you a range in five minutes. That speed will be important in 2026, when most teams are now demanding CAD-upload quoting and price feedback that will keep up with the spec changes, continuing to keep the iteration going.

We discovered that at our factory the quickest method of a simple mold becoming a high quality or premium mold is when the part must have side-actions to create an undercut, as well as when it requires a hot runner system to be efficient. In the meantime, we will disaggregate those cost triggers in the article. This is a budget range that you should take into consideration, though, since a real quote is still dependent on your CAD, tolerances, and target volume.
What Tooling Cost Actually Includes
Tooling cost is the one-time spend to build the mold itself. It covers the mold base and metal cutting such as CNC machining and EDM. Moreover, it also includes bench fitting, surface finishing, and tryout sampling runs. The common mold cost line-items are:
- Optional hot runner manifold and temperature controls.
- Mold steel grade selection.
- Sliders, lifters, or unscrewing mechanisms.
- Mold design checks and testing samples.
When geometry gets more multifaceted, the number of build hours increases rapidly, and this is the primary factor that an injection mold tooling cost calculator takes into account.
2026 Reality Check: Usual Mold Price Ranges
Prototype and Bridge Tools: Lower Entry Costs
For early tests and short runs, makers might consider using soft tools, printed inserts, or aluminum options. Along these lines, industry guides cite numbers from $100 for very low-volume printed tooling up to a few thousand dollars for simple aluminum molds.
Hardened Multi-Cavity Production Molds: When Costs Climb
When you move into long-life and high-output frameworks, costs can increase abruptly. Different sources note an injection mold price that can reach even more than $100,000 for complicated and multi-cavity steel tooling, particularly as requirements get higher.
The 5-Minute Injection Mold Tooling Cost Calculator
Step A: Choose Required Mold Life (SPI/Tool Class) (1 Min)
To start your injection mold tooling cost calculator, pick the tool class as per your demand. SPI classes entail prototype (Class 105, very short life), low volume (Class 104), medium volume (Class 103), and high volume (Class 102-101). Higher classes are for far more cycles and might need tougher materials and build standards, which eventually increases the budget.
Step B: Enter the 7 Inputs That Move Mold Price the Most (3 Min)
- Part size and projected footprint: Bigger parts need a larger tool frame and plates. That results in more cutting time and demands heavier handling.
- Part complexity: Thin ribs, deep pockets, and towering walls are more difficult to machine neatly. Additionally, it takes more time to fit and check them.
- Undercuts and side actions: Undercuts need slides, lifters, or an unscrewing arrangement. Similarly, even one side action can add a noticeable jump in cost.
- Cavity count: The initial tooling effort may increase if there are more cavities. In exchange, you may reduce part cost per shot when working with higher volumes.
- Runner system: Cold runners make tooling more straightforward. On the other hand, hot runners cost more at first but can save you money by minimizing scrap on large jobs.
- Tool material: Aluminum can be an intelligent choice for short programs. In comparison, hardened steel makes more sense when you want something to last a long time.
- Tolerance and cosmetic requirements: Narrow dimensions and high-polish surfaces harden the finishing workload. They also make extra tuning compulsory after trials.
Step C: Pick Lead Time and Risk Buffer (1 Min)
Now set your schedule, although with faster turnarounds come higher cost and priority in the shop. Guides say that an ordinary injection-molding process takes 6-10 weeks, but rapid programs can go from CAD to molded parts in 7-10 days. So, shorter lead times cost more.
Allow some small adjustment in the T1, which can be important since actual parts may show fit or cosmetic problems. A preliminary DFM check will reduce such shocks, and the second run of your injection mold tooling cost calculator will be very similar to the final quote.
A Worked Example
Consider a palm-sized ABS consumer housing. With a single-cavity tool, each cycle gives one part. Output builds slowly as quantities rise. However, with a 4-cavity version, the tool is pricier to make, but you get four parts per cycle. The cost per piece improves with higher volume.
According to one cavitation cost example, a 1-cavity mold at $5,000 vs. $12,500 for a 4-cavity mold. That direct gap is justified when you spread the tools out over a larger order.
Now, you can change your estimate while adding just a side snap feature. That small variation can make an undercut, which might need a slide or lifter. The tools can cost more because of these mechanisms. To learn how to estimate mold price, divide the mold cost by the planned output. This will give you a simple per-part number for the tooling burden.
Biggest “Hidden” Tooling Cost Drivers and How to Reduce Them
Design-Side Fixes That Quietly Cut Cost
If your injection mold tooling cost calculator number is high, you may look for features that trap the part during ejection. Those force extra moving hardware in the tool. Hence, redesigning snaps, holes, or recesses to pull straight can lower risk and spend. Cleaning up purely cosmetic details also helps. That’s because premium finishes increase more hand work than people expect.
Tooling Strategy That Fits Your Forecast
A softer tool can be quicker and cheaper to change than a fully hardened one for pilot builds and ramps. On the other hand, hardened tooling makes more sense when demand is stable and high because it is supposed to last longer. You don’t have to pay for durability you don’t need if you choose the lightest SPI class that still remains at your expected cycle count.
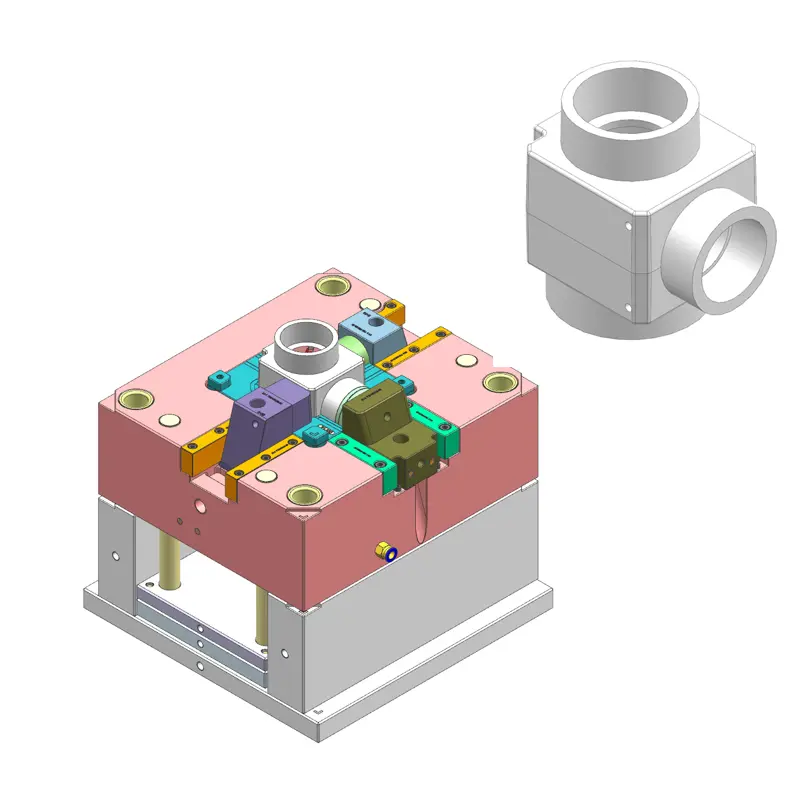
Upload CAD for Fast DFM Feedback
One way to confirm feasibility and cost is to send your CAD for a DFM pass. A good DFM report flags moldability risks such as draft, parting lines, thickness, and tolerance before you commit. That prompt feedback can help avoid late-stage changes that inflate the tooling plan.
What We Need To Turn Your Estimate Into A Quote
Need quote from an injection mold tooling cost calculator estimate? We keep it simple. Please provide your 3D CAD file (STEP/IGES), 2D drawing (with the tolerance notes), preferred resin mixture, anticipated order quantity, desired type of mold, etc. In case you could state any extraordinary needs like export packing or long-term support in terms of moldings, we can be able to settle pricing within a lesser amount of time and get back with feedback.
Data Sources:
https://formlabs.com/global/blog/injection-molding-cost/
https://www.fictiv.com/articles/rapid-injection-molding-the-ultimate-guide
https://www.basilius.com/blog/understanding-the-cavitation-cost-benefit-analysis/





