Various types of molds can be used to manufacture medical devices, including injection molding, blow molding, and thermoforming.
Injection molding is a process in which melted plastic is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. This process often creates large volumes of identical parts with high precision and tight tolerances. Injection molding is commonly used to produce medical devices such as syringes, vials, etc.
Blow molding is when a molten plastic tube is placed in a mold, and the air is blown into the tube to form the desired shape. This process often creates hollow medical devices such as bottles, containers, and tubing.
Thermoforming is a process in which a plastic sheet is heated until it becomes pliable and then formed into the desired shape using a mold. This process often produces medical devices such as trays, packaging, and protective covers.
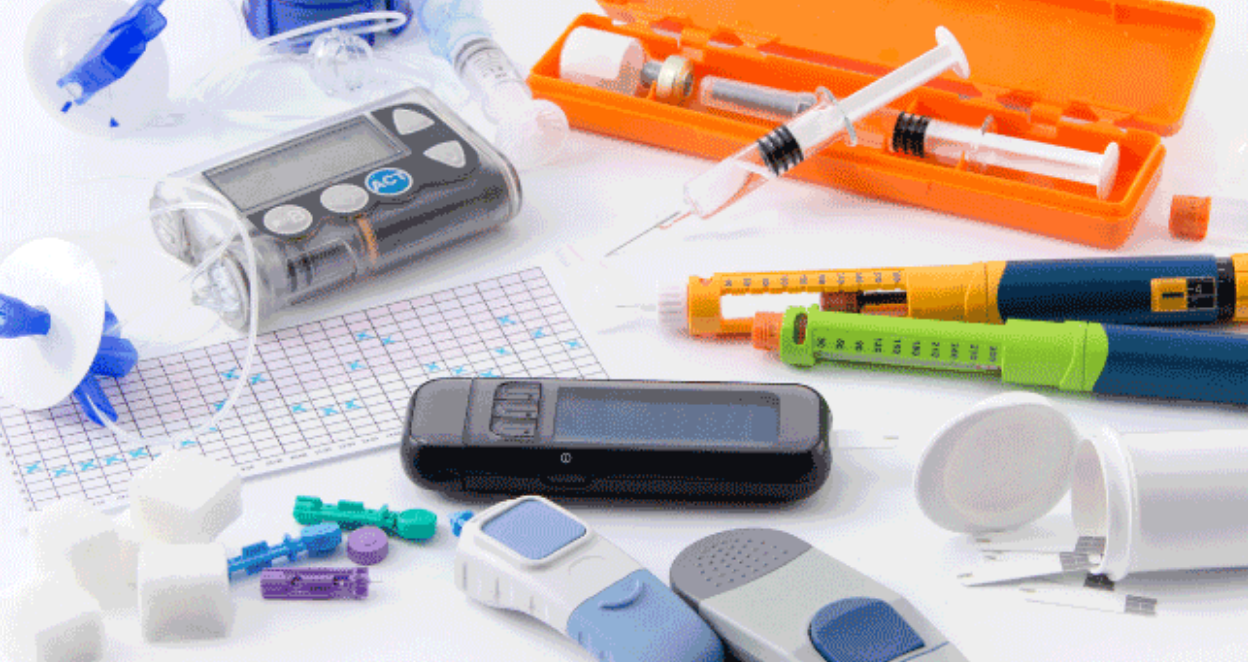
Types of injection molding for medical:
Standard injection molding is the most common type used to create a wide range of plastic parts and products.
Two-shot injection molding: This process involves injecting two different materials into the same mold to create a single part. This is often used to create parts with multiple colors or to combine different materials with different properties.
Insert injection molding: This process is putting the metal insert into the same mold to create a single part; most of them are used for connectors.
Overmolding: This process involves injecting a second material over a previously molded part to create a finished product. This is often used to create grips, handles, and other functional features on products.
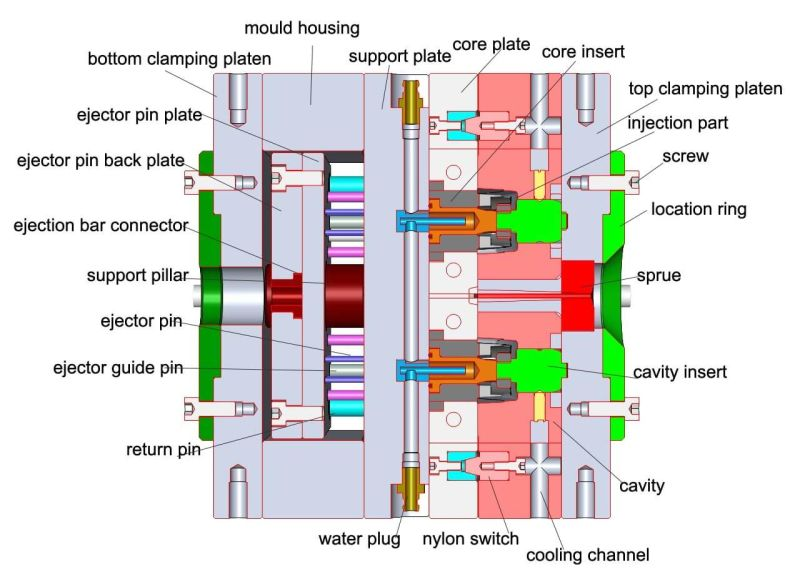
Plastic injection mold styles:
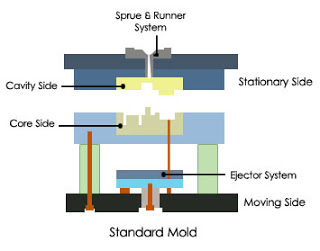
2plate mold: Two plate mold is the easiest injection mold structure with many advantages. It’s consisted of a fixed side(Cavity) and a movable side(Core) with 2 main parts. In the structure of two plate mold gates, sprue, runners, and cavities are all on the same side. In a multi-cavity two-plate mold, gates and runners must be in the parting line to be easily ejected when the mold splits. And two-plate mold has many benefits and drawbacks. It could add more complex structures, like sliders, angle sliders, lifters, and angles, etc., to achieve the product’s structure.
The advantages Of Two Plate Mold
Shortened molding cycle and long life span
Simple design and easy to operate
Cheaper to manufacture than a three-plate mold
More comfortable to select gate location and shape
Minimal operational difficulties & less maintenance
3plate mold: Three plate injection mold consists of two parting planes and splits into three sections. Therefore runners and components can be located on different parting planes. The runner is ejected separately to the molded part in three plate molds. Therefore automatic de-gating is possible. Its application includes positioning the runner system in different planes to injection location and automatic de-gating. Three plate mold will open two steps to achieve some function or requirements of the plastic molding part. Add components like point gates, cavity sliders, etc., to achieve the different steps. And could add more complex structures, like sliders, angle sliders, lifters, angles, etc., to achieve the product’s structure.
The advantages Of three Plate Mold
Flexibility in gating location.
Low-cost alternative to hot runner mold.
Eliminate gate removal operation.

Reverse mold: Reverse mold is to turn around the mold and inject from the ejector side. This structure needs to consider how to eject the products, then add two cylinders on eject plates to achieve this function.

Talking from runner types, there have cold runner systems and hot runner systems:
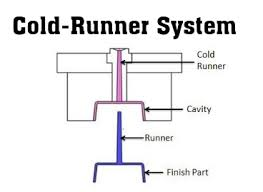
Cold runner system: Cold runner is after injection molding machine melt are the runner at the mold steel, normally, cold runner with long runner and waste much raw material, reducing the molding pressure.
In a cold-runner mold system, the runner has to be larger than the part. Otherwise, you run the risk of underfilling the mold. One big advantage over a hot-runner system is the ability to use more types of polymers without concern for heat sensitivity.
Cold runners are less expensive than hot runners and are easily maintained as well, but they can create waste unless you can recycle or melt down the extra material.
Hot runner system: Hot runner system means an added heating system in the mold. Hot runners are more expensive than cold runners (in initial investment and maintenance), but they can handle higher volumes and larger parts and don’t generate waste. In some cases, the lack of waste balances with the higher maintenance cost to be about the same net cost as a cold-runner system. Hot-runner molds produce parts with more consistent quality and do so with faster cycle times, but it’s not as easy to change colors, nor can hot runners accommodate some heat-sensitive polymers.