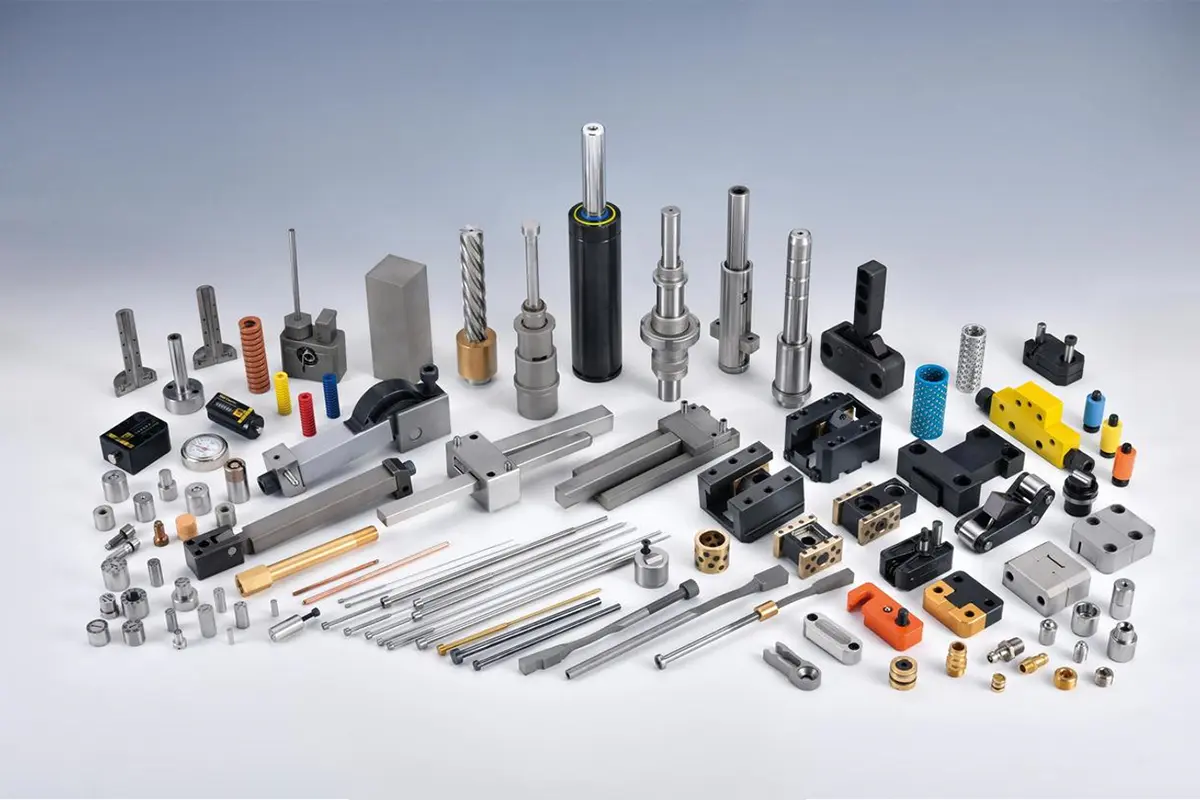
Standardization of injection mold components is crucial for enhancing manufacturing efficiency and ensuring product quality. These standardized components regulate mold design, manufacturing, and usage, guaranteeing compatibility and consistency across different regions and industries. Currently, the internationally recognized mold standards primarily fall into three major categories: DME standards, HASCO standards, and MISUMI standards. Below is a detailed introduction to these standards:
DME Standard:
The DME (Division of Mold Essentials) standard is an American mold component specification covering a broad product range, including mold bases, ejector pins, guide pins, and bushings. Its key feature is the use of both metric and imperial unit systems, making it easy to apply globally. The DME standard is trusted globally within the mold industry for its excellent interchangeability and wide applicability.
HASCO Standard:
Originating in Germany, the HASCO standard is one of the global production standards for mold components. Emphasizing component compatibility, design simplicity, and operational convenience, it has rapidly gained traction in international markets. HASCO establishes stringent requirements for mold component design, dimensions, functionality, and material selection, ensuring high-quality parts and consistent performance.
MISUMI Standard:
The MISUMI standard, developed by the Japanese company MISUMI, primarily offers customized mold component services. This standard also emphasizes interchangeability and high precision, making it widely adopted in Asian markets. Its strength lies in providing flexible solutions through innovative designs tailored to specific customer requirements, thereby accelerating production cycles.
Other Relevant Standards:
Beyond these three major standards, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has established a series of mold-related standards to promote global consistency and interchangeability. Examples include ISO 20457 (DIN ISO 20457—focusing on specific requirements for injection molds). These standards primarily cover mold design, manufacturing, inspection, and usage, further ensuring the quality and safety performance of mold products. Furthermore, countries maintain their own national standards, such as Japan’s JIS standards and Germany’s DIN standards, which influence the global mold industry to varying degrees.
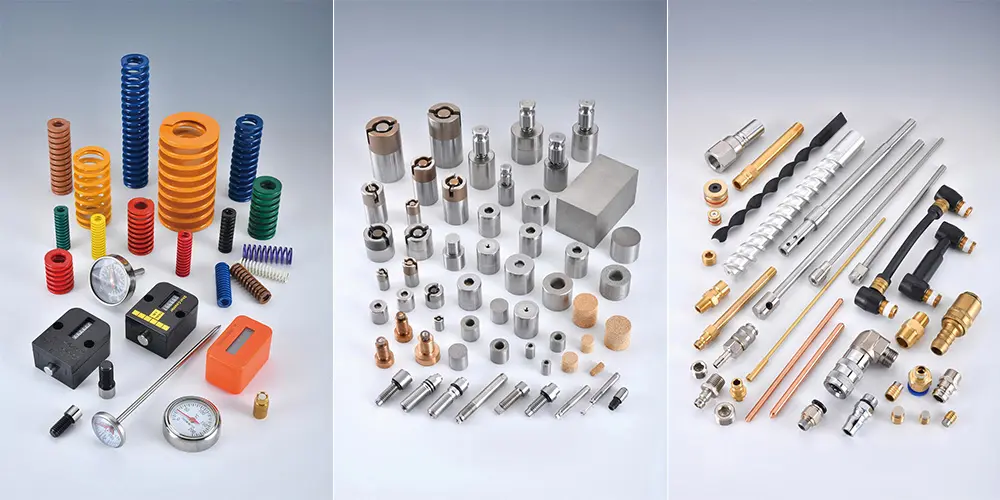

The global standardization system for mold components continues to evolve, with diverse standards complementing each other to create a multifaceted manufacturing environment. This facilitates international trade and efficient collaboration, ensures seamless integration of mold components across multinational production lines, and elevates the industry’s overall technical standards and competitiveness. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers can ensure their products meet international market requirements, reducing uncertainties in design and production processes.
In global applications, standard selection is largely based on regional and customer needs. For example:
Western countries, particularly North America, tend to favor DME standards.
Europe predominantly uses HASCO standards.
Japan and other Asian regions rely more heavily on MISUMI standards.
Within the international mold component standards framework, attention should also be paid to the development of digitalization and smart manufacturing. These emerging trends are driving the evolution of mold standards. For instance, the ISO 20457 series standards not only address traditional mold design and manufacturing but also incorporate digital standards to meet the demands of modern intelligent production, thereby enhancing injection mold precision and production efficiency.
Furthermore, national mold industry organizations are actively promoting the alignment of local standards with international standards to facilitate the integration and coordination of the global mold market. China’s mold industry standards, such as GB/T 15141-2013, are progressively aligning with international norms to enhance competitiveness.
These standards encompass not only mold design, manufacturing, and material performance requirements but also extend to environmental protection and sustainable development issues, addressing global resource scarcity and ecological challenges. While these trends complicate standard development, they also render it more comprehensive and forward-looking…