The cutting tool industry is predicted to rise from 75,715.2 billion in 2024 to USD 1,17,083.1 billion by 2032. This industry is growing rapidly with its increasing demand for metalwork. Factors like trends, technology (AI, 3D printing) and globalization significantly influence its growth.
Here we highlight some important factors, from emerging technologies to skill development. That further clarifies the future of the cutting tool industry.
Overview of the Current State of the Cutting Tool Industry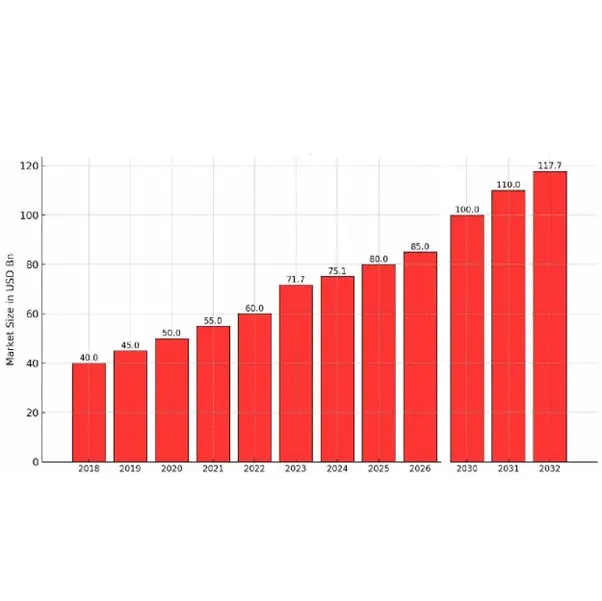
You will get to know the manufacturers used to cut material with primitive hand tools. That was crafted with stone and metal. The need for precision and surface finishes converts these outdated methods into evolving technology.
With the passage of time, researchers break the disruptive technology into inventions of steam-powered tools and later electricity. Nevertheless, carbide tools proved beneficial. That sway more advanced technology like CNC machines with automotive features.
Key Players and Market Leaders
For ages, some prominent global leaders, Sandvik, Kennametal, and Mitsubishi, have brought remarkable changes in conservative methods. They innovate the designs of tools, material science, and adeptness.
The entire cutting tool industry owes these key players. Their tireless efforts set the benchmark of quality and implementation. As a result, small to large-volume industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics saw the advent of modern cutting machines.
Recent Trends and Challenges
Today, the industry of cutting tools relies on digital technologies. The integration of AI-driven systems and IoT (internet of Things) offers collective manufacturing processes. They efficiently predict analytics and monitor the entire fabrication.
In addition, the cutting machine industry is emerging automotive technologies to detect faults in microseconds. It provides backing to produce the parts with a speedy process and error-free. However, some other factors, like raw material cost and supply chain, are still the center of discussion. They may affect the budgets and availability.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies
The cutting tool industry is progressing gradually. The new technologies are introduced with efficacious focus. That caters to designs, functionality, and desired output results.
Digital Transformation
- AI and Machine Learning
- IoT and Predictive Maintenance
- Digital twins and simulation
AI and Machine Learning
The integration of artificial intelligence in the cutting tool industry simplifies the difficult task. These significant components can provide precise measurements. They further aid the process of tool performance prediction, design accuracy, or material aspects.
Similarly, machine learning programs can detect tool faults and analyze vast datasets. They allow you to produce parts quickly by adjusting the machining factors.
IoT and Predictive Maintenance
IoT devices are connected to the internet. They collect real-time data by collaborating with sensors and software. These devices can aid unplanned manufacturing processes. The manufacturer can create distinctive schedules, maintain vast data, measure present temperatures, etc.
Moreover, IoT technology shows vibration and load capacity supporting performance analysis. It can provide budget plans, cost assessments, and production estimations.
Digital twins and simulation
Digital twins represent the performance of any task, object, or process in the real world. They demonstrate how the object will perform. Like jet engines, wind farms, or building structures.
Conversely, the simulation indicates the model environments under varied conditions over time. However, both factors collect real-time data for testing designs and troubleshooting faults before production. These technologies reduce processing time and material waste.
Advanced Materials
- Superalloys and Ceramics
- Nanocoatings and Surface Treatments
- Additive Manufacturing
Superalloys and Ceramics
Supperalloy includes cobalt and nickel compounds and many others besides. They fight against harsh environments. These alloys provide oxide layers to machining tool parts as a barrier. That diffuses oxygen and prevents the propagation of rust, corrosion, or oxidations.
Ceramics are the non-metallic components. They are available in crystalline or glassy form. It makes the parts strong and resists heat. You can use them to make tough mashups like titanium and nickel for electronics and automotive applications.
Nanocoatings and Surface Treatments
Applying nanocoating and surface treatment to tools increases their longevity. TiN coatings, or DLC (diamond-like carbon), are the executive innovations that minimize friction. It reduces wear and treats heat dissipation. These technologies do not let the tool degrade under challenging situations.
Additive Manufacturing
3D printing and cutting tools can create generative designs with clear details. It can balance the performance of parts, reducing material waste. The new improvements in this segment accelerate the machining cycles and align sustainable manufacturing practices.
Industry Trends and Market Dynamics
- Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
- Sustainability and Green Manufacturing
- Global Supply Chain and Trade
Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
The Industry 4.0 revolution is the integration of intelligent digital technologies with manufacturing sectors. This rule is also known as 4IR. It encompasses several networks. For instance, interoperability, IoT, augmented reality, cloud computing, etc. In the cutting tool industry, 4IR is embedded with smart sensors. They monitor real-time functionality to predict maintenance and unplanned downtime.
Data-Driven Decision Making
AI systems can manage large data sets. It helps in considering material selection. These devices further make it easy to assess operations cost, performance efficiency, and future difficulties before production.
Sustainability and Green Manufacturing
Eco-Friendly Materials and Processes
Modern cutting tool machines enable sustainable practices. They allow the manufacturers to use eco-friendly alloys as substitutes. In this way, they can reduce the footprint of material.
Circular Economy and Tool Recycling
Circular economy is an innovative model. That plays along with the repeated cycling process of cutting tools. These models are subject to reducing material waste and promoting sustainable resources. The manufacturers can keep the products to use them for a long time. For this, the object is processed under various methods of recycling, repairing, reshaping, etc.
Global Supply Chain and Trade
Geopolitical Factors and Trade Disputes
Geopolitical factors and trade disputes cause raw material shortages. the manufacturers are investing in a global hub, building the supply chain resilience. They diversify their supplier base and surge the flexibility in outputs. Additionally, the advanced inventory systems also address severe risks.
The Future Workforce and Skill Development
The future workforce and skill development raise the scope of the cutting tool industry. Specialized tool skills help in operating complicated or advanced techniques.
The Role of Human Workers in an Automated Future
Humans are investing in automated skills and robotics devices. It ensures the metalworker is equipped to operate and handle advanced cutting tools. This expertise helps them find the problem in the exact areas where adjustments are needed.
Human-Robot Collaboration
The human-robot collaboration (cobots) brings prominent changes in cutting tool performance. Cobots maintain the various tasks all at once, handling the repetitive process of tough materials. It can control the hazardous paces focused on higher-level decision-making.
Education and Training
Developing the Next Generation of Tool Engineers
The engineers must tap into diverse universities and research centers. Where they can find the unique talent that aligns with the evolving needs of cutting tools. So that they can execute advanced tools.
Continuous Learning and Professional Development
Continuous learning expands the knowledge of engineers. They can locate and resolve the technical issues of advanced tools. The operators can also embrace lifelong education from various sources. For instance, workshops and e-learning. They can master the new tools, processes, and upcoming technology.
Conclusion
Changes in cutting tools and innovations in smart technology influence the cutting tool industry. The introduction of AI, automotive devices, robots, and sustainable material choices are the evolving parameters. These innovative techniques ensure the stable operation of production lines. On the path of technological development, precision results, downtime, and cost analysis-like factors predict this industry will be a great mechanism for improving productivity in the future.





